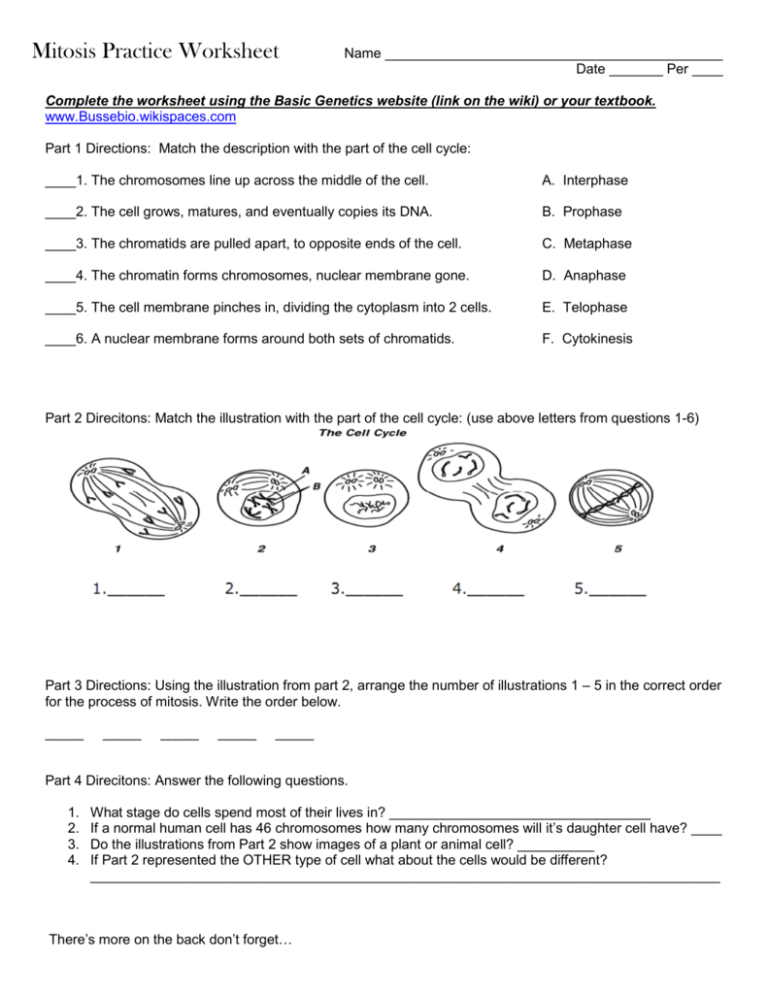
As an organism matures it needs to replace worn-out cells. The cell grows matures and eventually copies its DNA.
How Does Dna Make New Cells Quora
The chromatids are pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell.
. In eukaryotes the cell cycle is more complicated. Stuctures called spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends. The nuclear membrane breaks down.
Where the cell grows to its mature size makes a copy of its DNA and prepares to divide into two new cells. By observing the chromosome one can identify the mitotic process. The cell cycle is a repeating series of events that include growth DNA synthesis and cell division.
During interphase the cell grows and DNA is replicated. In eukaryotes the cell cycle is more complicated. As an organism matures it needs different kinds of cells.
The Cell Cycle By Liam Stapley 11062018 Stage 1. Which substage of interphase is where the cell copies its DNA in preparation for cell division. This stage of the cell cycle is when the cells nucleus divides into 2 nuclei In this phase cytokinesis begins The cell cycle results in two genetically _____ daughter cells In this cell cycle phase the cell grows to its full size copies the DNA and.
First stage of the cell cycle during which a cell grows matures and replicates its DNA Anaphase third stage of mitosis in which sister chromatids are pulled apart and microtubules along with motor proteins move the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. It is divided into three phases - G1 S and G2. The cell undergoes nucleus division and split into two identical daughter cells.
Eventually the parent cell will pinch apart to form two identical daughter cells. The cell grows its DNA replicates and the cell divides. Each cell that is actively dividing eventually copies its DNA and.
First stage of the cell cycle during which a cell grows matures and replicates its DNA Anaphase third stage of mitosis in which sister chromatids are pulled apart and microtubules along with motor proteins move the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. The cell cycle has two major phases. 3The cell grows matures and eventually copies its DNA Longest phase.
However some cells stop the cell cycle at the G 1 stage. The chromatids are pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell. The cell grows its DNA replicates and the cell divides.
Most cells continue the cell cycle. The chromatin in the nucleus condences to form chromosomes. The stages of mitosis occur in sequence with specific events in each one.
Cell division is just one of several stages that a cell goes through during its lifetime. You just studied 25 terms. Prophase The chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes.
This form of division in prokaryotes is called asexual reproduction. Phases of interphase Stage 2. The chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell.
Interphase is the stage in which the cell grows matures and replicates its DNA. Mature nerve cells in your brain remain in G1 and do not divide again. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth DNA replication and division that produce two genetically identical cells.
The division of the cytoplasm following mitosis resulting into two identical copies of the originelle cell called daughter cells. As an organism matures it needs to replace the DNA in each of its cells. Now up your study game with Learn mode.
The spreading of cancer cells through the circulatory system blood vessels and lymph nodes that allows tumors to grow in other organs. Interphase The cell grows to a mature size makes a copy of its DNA and prepares to divide into two cells. The structure of coiled DNA and proteins that forms in the cells nucleus prior to mitosis is.
The cell cycle is a repeating series of events that include growth DNA synthesis and cell division. The cell membrane pinches in dividing the cytoplasm into 2 cells. But at both ends of each chromosome there is a long piece of DNA that doesnt code for anything.
Most cells makes proteins needed for DNA. To make more cells one cell copies its DNA and divides into two cells. Each of the two daughter cells ends up with one copy of the DNA.
The cell cycle in prokaryotes is quite simple. During this phase the cell grows rapidly reaching its mature size while performing routine metabolic processes. The majority of the cell cycle where the cell grows matures and eventually copies its DNA.
Strands of chromatin are copied so there are now two identical strands of DNA. Cells do not copy their DNA and do not prepare for cell division. A cell grows and carries out its normal cell functions.
5The chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell. A nuclear membrane forms. The chromatin forms chromosomes nuclear membrane gone.
During interphase the cell prepares itself for. Interphase and the mitotic phase Figure 63. The cell grows matures and eventually coppies its DNA.
As an organism matures it needs more cells. Remember that the DNA is in the nucleus which is. The cell cycle in prokaryotes is quite simple.
Most of the DNA in each cell has important instructions in it. Mitosis steps consist of prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. Mature nerve cells in your brain remain in G 1 and do not divide again.
This is necessary because each new cell gets a copy of the genetic information. The S Stage During the S stage a cell grows and copies its DNA. The first stage of the cell cycle during which the cell matures grows and prepares to divide and copies its DNA.
Structures called spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell.

Cell Cycle Mitosis Asexual Regulation Cancer Quiz Quizizz
Cell Cycle Dna Replication Centrosomes Centrioles And Cell Division Springerlink
0 Comments